MESOC
1) Health and Wellbeing,
2)Urban and Territorial Renovation and
3)People’s Engagement and Participation.
The global aim is to respond to the challenge posed by the H2020 Call ”To develop new perspectives and improved methodologies for capturing the wider societal value of culture, including but also beyond its economic impact”
MESOC SERAPEUM
Project idea is to enable
MESOC consortium members and other cultural stakeholders to become acquainted with the
achievements of artificial intelligence and gain insight into the possibilities of AI. It is
work in progress and will be updated regularly.AI tools are especially used to identify
transaction variables that define contextualisation of research findings.
MESOC SERAPEUM
Project Statistics

1526
Scientific papers analyzed
6561
Candidate transition variables extracted
130
Taxonomy terms defined
410
Impacts screened
SEARCH
Search the documents on cultural artifacts
Semantic search
Semantic search on articles. Semantic search describes a search engine’s attempt to generate the most accurate search engine results possible by understanding based on searcher intent, query context, and the relationship between words.Semantic search denotes search with meaning, as distinguished from lexical search where the search engine looks for literal matches of the query words or variants of them, without understanding the overall meaning of the query. Some authors regard semantic search as a set of techniques for retrieving knowledge from richly structured data sources
Analysis
Analysis of documents with Artificial Intelligence
The system reviews documents to assess the social impact of culture. The review includes analysis of all and individual documents, clustering, summarizing, keyword analysis, and other analytical tools and methods.
Particular Document Analysis
Document analysis : resolving study technique, key phrases, keywords, summary for article, finding article's cultural category and social impact, ask questions on article, showing wordcloud, finding similar articles from same cluster
Documents cluster analysis
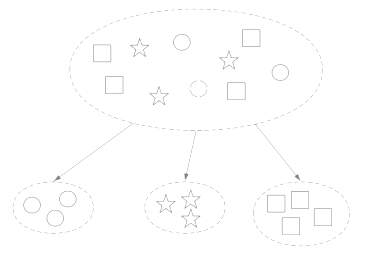
Text clustering is the task of grouping a set of texts in such a way that texts in the same cluster are more similar to each other than to those in other clusters. Text clustering algorithms process text and determine if natural clusters (groups) exist in the data.
As computers work with numbers, text has to be transformed into multidimensional numbers as vectors. We use here 4096 dimensional space.The idea is that documents can be represented numerically as vectors of features. The similarity in text can be compared by measuring the distance between these feature vectors. Objects that are near each other should belong to the same cluster. Objects that are far from each other should belong to different clusters
Topic model is a type of statistical model for discovering the abstract "topics" that occur in a collection of documents. Topic modeling is a frequently used text-mining tool for discovery of hidden semantic structures in a text body.
TRANSITION VARIABLES
contextual elements, which can be measured ensuring that the cultural policy or practice under inspection is generating public value and/or affecting, at least to some extent, the target individuals or groups.
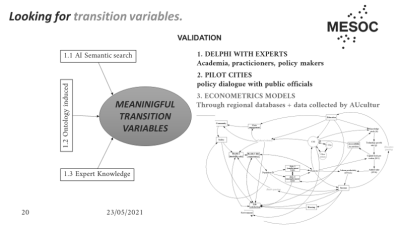
Transition variables show us the paths of transformation and the channels of materialization of the impact, in a richer and more complex analysis than the cause-effect linearity.
Transition processes are complex and non linear, but induce changes across time.
Transition variables enable a better contextualisation of the concrete processes in concrete places and periods.They can be observed in shorter periods of time than the expected impacts.
We can obtain them from the experiences recorded in scientific literature and in grey material reports (evaluation reports, memos, programs...)
.Transition variables search and view
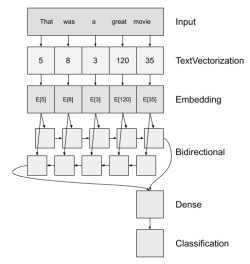
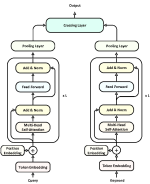
We are using a pre-trained BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) model for a text classification task. The main goal of the model in a text classification task is to categorize a text into one of the predefined labels or tags, and in our case to read sentences and to classify them as normal sentences or potential transition variables.
BERT is pretrained on unlabeled data extracted from BooksCorpus, which has 800M words, and from Wikipedia, which has 2,500M words. We are fine-tuning it, by training on our sample of 3500 sentences each of which is manually marked, as trans. variable or anything else.
Social impact transition variables
Search and view of transition variables based on social impact
Cultural domain transition variables
Search and view of transition variables based on cultural domain
Combined transition variables
Search and view of transition variables based on cultural domain and social impact
SOCIAL IMPACTS
Transformative process - Using AI to define social impacts
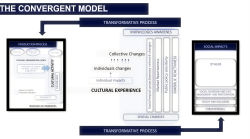
‘Social impacts’ is the term which describes the changes in the quality of life of the local residents. Changes that affect individuals’ surroundings (architecture, arts, customs, rituals etc.) constitute cultural impacts.
The enormous range of impacts include arts and crafts through to the fundamental behaviour and beliefs of individuals and collective groups (Sharpley, 2008; Sharpley & Telfer, 2014).
.